Triglycerides are a form of fat (lipid) in your blood, and they have a vital role to play in the energy metabolism of your body. But if levels become too high, they can raise your risk of heart disease and other health issues. In today’s day and age, with lifestyle diseases on the rise, it is important to learn about how triglycerides work and how to control them to keep your heart healthy. This article describes what triglycerides are, their impact on your health, and how medications manage high levels.
What Are Triglycerides?
Triglycerides are fats that your body gets energy from. When you eat, your body stores the calories it doesn’t immediately use as triglycerides in your fat cells. Hormones then release these triglycerides for energy between meals. Triglycerides are healthy when used in moderation, but too many in your blood can be harmful. When triglyceride levels rise too high, healthcare providers might suggest aztor 40 tablet to help bring them back to a healthier range.
How Are Triglycerides Different from Cholesterol?
While both are forms of lipids in your blood, triglycerides and cholesterol are distinct.
- Cholesterol is utilized to construct cells and hormones.
- Triglycerides are utilized as fuel.
- Both pass through your blood in the form of lipoproteins, but elevated levels of either will enhance your risk for heart disease.
What Are Normal Triglyceride Levels?
Triglyceride levels are defined by the American Heart Association (AHA) as:
- Normal: Less than 150 mg/dL
- Borderline High: 150–199 mg/dL
- High: 200–499 mg/dL
- Very High: 500 mg/dL or higher
Having triglycerides in the normal range is essential to lower heart disease risk.
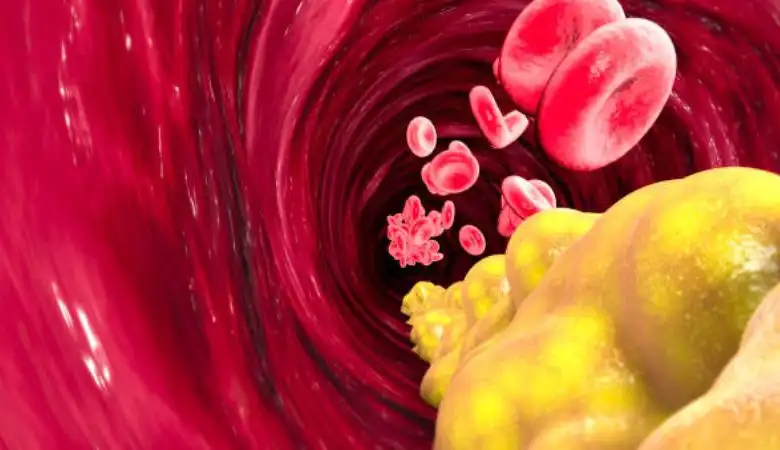
Why Are High Triglycerides Dangerous?
High triglyceride levels (also referred to as hypertriglyceridemia) can cause:
- Hardening, or hardening of the walls of the arteries (atherosclerosis), which raises the danger of heart attack and stroke
- Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), especially at extremely high levels
- Higher risk of developing metabolic syndrome—a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, increased fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol
- These risks necessitate frequent checking and controlling triglyceride levels.
Causes of High Triglycerides
A number of causes can lead to elevated triglycerides:
- An unhealthy diet, particularly high in sugars and refined carbohydrate
- Obesity and a sedentary lifestyle
- Heavy drinking
- Medically, conditions like type 2 diabetes, hypothyroidism, or kidney disease
- Certain medications, such as steroids, beta-blockers, and diuretics
- Genetic conditions affecting lipid profiles, including familial hypertriglyceridemia
By correcting the underlying cause through dietary changes or medications, triglycerides can be controlled successfully.
Signs and Symptoms
High triglycerides typically do not have symptoms. However, in extremely high levels, signs and symptoms might be experienced as follows:
- Under-the-skin fatty lumps (xanthomas)
- Pancreatitis, with signs and symptoms of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting
- Higher risk of cardiovascular incidents, like angina or heart attack
- That’s why early detection is crucial with regular blood tests.
The Connection Between Triglycerides and Heart Disease
Elevated triglyceride levels may lead to atherosclerosis, in which plaque accumulates in the arteries. This causes the arteries to constrict and lower blood supply to the heart and brain, putting one at risk of heart attacks and strokes. Furthermore, high triglycerides typically coexist with other risk factors like low HDL (good cholesterol), high LDL (bad cholesterol), and high blood sugar levels, all of which heighten the likelihood of heart disease.
How to Reduce Triglycerides Naturally
Following are some lifestyle modifications that can lower triglycerides significantly:
1. Enhance Your Diet
- Reduce sugar and refined carbohydrates such as white bread and pastries.
- Steer clear of trans fats and minimize saturated fats.
- Consume more fiber, particularly from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Boost omega-3 fats, present in fish such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
2. Practice Regular Exercise
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity five days per week. Exercise burns triglycerides for fuel.
3. Reduce Excess Weight
A weight loss of as little as 5–10% can lower triglyceride levels dramatically.
4. Cut Back on Alcohol
Alcohol contains many sugars and calories and directly affects triglyceride levels.
5. Control Blood Sugar
If you have diabetes, manage your blood sugar. Excess glucose will raise triglycerides.
Medications That Assist in Reducing Triglycerides
If lifestyle modifications are not sufficient, physicians might prescribe medications to reduce triglyceride levels and safeguard the heart.
Aztor 40
Aztor 40 has atorvastatin, a statin medication that lowers LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. It operates by decreasing the liver’s production of cholesterol, which in turn decreases triglyceride levels. Aztor 40 is usually prescribed for individuals who are at high risk for cardiovascular events and particularly have diabetes or a history of coronary artery disease.
Lipvas 10 Tablet
Lipvas 10 Tablet also includes atorvastatin and is similar to Aztor 40. It reduces triglycerides and bad cholesterol but raises HDL (good cholesterol). Lipvas is generally considered as part of long-term treatment to control lipid disorders and avert heart attacks and strokes.
Lipvas 10 Tablet should be taken in accordance with the prescribed dosage. They are best when followed by diet and lifestyle changes.
Side Effects of Statins
Although statins such as Aztor 40 and Lipvas 10 Tablet are safe, they can cause:
- Muscle pain or weakness
- Digestive problems
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Increased risk of diabetes in rare cases
- Report all side effects and unusual symptoms to your doctor at all times.
Monitoring Your Triglycerides
Routine lipid profile checks are necessary to keep your triglycerides and cholesterol levels in check. Adults aged 20 and older need to have a complete lipid panel every 4–6 years. If you have a personal or family history of heart disease or other risk factors, regular testing may be required more often.
Last Thoughts
Triglycerides can be just another statistic on your blood test results, yet they are a critical measure of your heart health. If left untreated, high triglycerides can lead to major illnesses such as heart attacks, strokes, and pancreatitis. But with lifestyle adjustments and medications such as Aztor 40 and Lipvas 10 Tablet, you can control your triglyceride levels and shield your heart for the long run. Choose heart-friendly options today and consult with your physician on the best course for you.